High Performance Computing For Lebanon (HPC4L)
Lebanon joined the CERN family in 2016 through the signature of an International Cooperation Agreement. This triggered a strong development of the country’s contributions to CERN projects, particularly through the affiliation of four of its top universities to the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment. Despite the challenges occurring in Lebanon, the Lebanese scientific community has reaffirmed its commitment to CERN and CMS.
To support Lebanese academics a technology transfer project has been initiated to build up the research capacity of the country. HPC4L will be the first High Performance Computing (HPC) facility dedicated to research of the country. HPC4L will provide computing capacity to support various research activities, including High Energy Physics and other scientific disciplines. HPC4L will make use of servers donated by CERN and a dedicated Lebanese support team trained by CERN and CMS HPC experts. HPC4L will bring together top higher education institutions (Public and Private) and will serve as a coordination hub for cooperation and communication across local key research players.
What is High Performance Computing (HPC)?
HPC refers to the practice of grouping computing power to perform complex computational tasks at a much faster rate and with greater accuracy than traditional computing systems. HPC centers operate similar to how a hive of bees work together to efficiently complete complex tasks. HPC enabling scientists and researchers to perform complex simulations and calculations faster.
HPC systems have helped accelerate scientific research in various fields by allowing researchers to perform complex simulations and modeling more efficiently.
CERN's data center is the heart of its operations. 450,000 processor cores and 10,000 servers hosted in three rooms are used 24/7 for scientific data management, email, and videoconferencing.
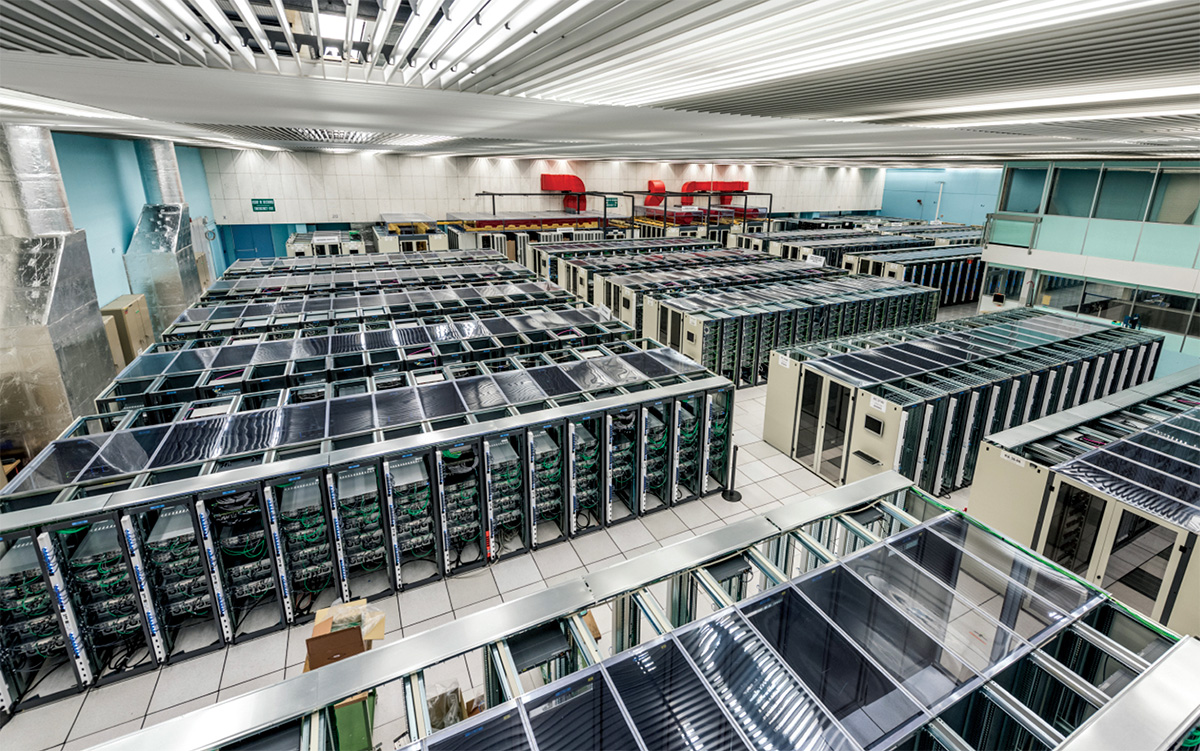

HPC4L x CERN
CERN stands for European Organization for Nuclear Research, which is the largest research organization in the world dedicated to the study of particle physics.
Scientists at CERN use the world's largest and powerful particle accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), to recreate the conditions that existed in the early universe moments after the Big Bang, to get closer to uncovering the secrets of the universe.
The LHC accelerates protons to more than 99.99% the speed of light and collides them at different experiments. At peak performance there are one billion proton-proton interactions per second and only 100 of these events get chosen from analysis. Even after this filtering process, CERN is expecting to gather 50 petabytes of data which is roughly equivalent to 2500 years of HD movies.
Analysing this amount of data requires a very large and expensive computing centre. In 2002 CERN started sending its data for analysis around the world creating the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG).
The WLCG consists of 170 computing centres in more than 40 countries with the aim of analysing, distributing, and storing the data coming from the LHC.
HPC4L will be part of the CMS WLCG as a Tier 2 computing centre, analysing data to help discover the secrets of the universe
Outreach and Media
You can learn more about HPC4L by watching our documentary and following our Instagram Account:
HPC4L's story has also received global media attention, here are some of our articles:
Articles about the inauguration event:
